Dataset View is a flexible tool that can help the User to detect anomalies and exceptions in the Datasets. This article describes Dataset Viewer settings in detail.
Table of contents:
1. Fields Selection
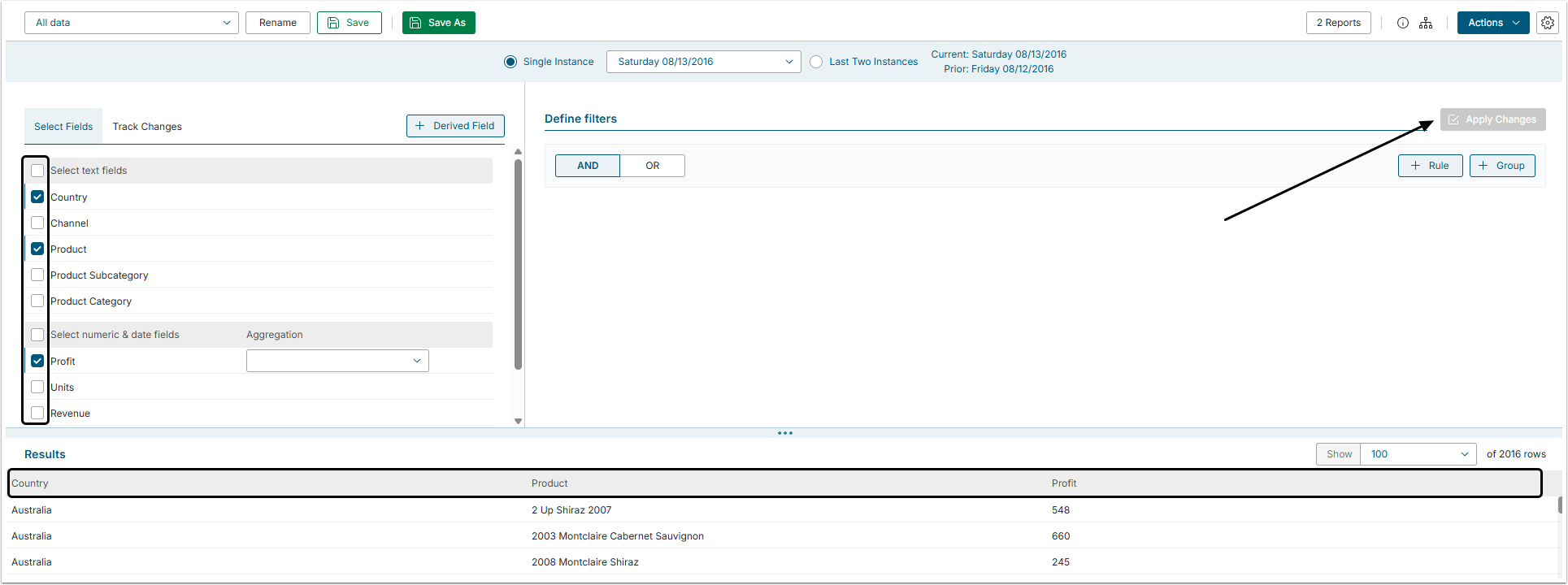
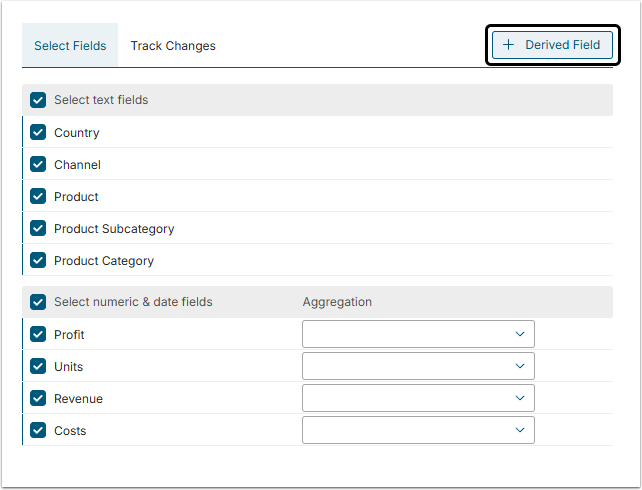
You can limit the display of Dataset's All Data only to those fields that are required for your data analysis.
Just select the fields you need in the Select Fields section, click [Apply Changes] in the right side of the screen and the Result set is going to be updated and only those columns that you have selected are going to be displayed.
2. Adding Derived Fields to Dataset's Result Set
Derived fields include values that do not exist in a Data Source itself but are calculated from one or more existing numeric fields via basic arithmetic expressions and non-aggregate numeric functions.
For more details refer to:
3. Defining Filters
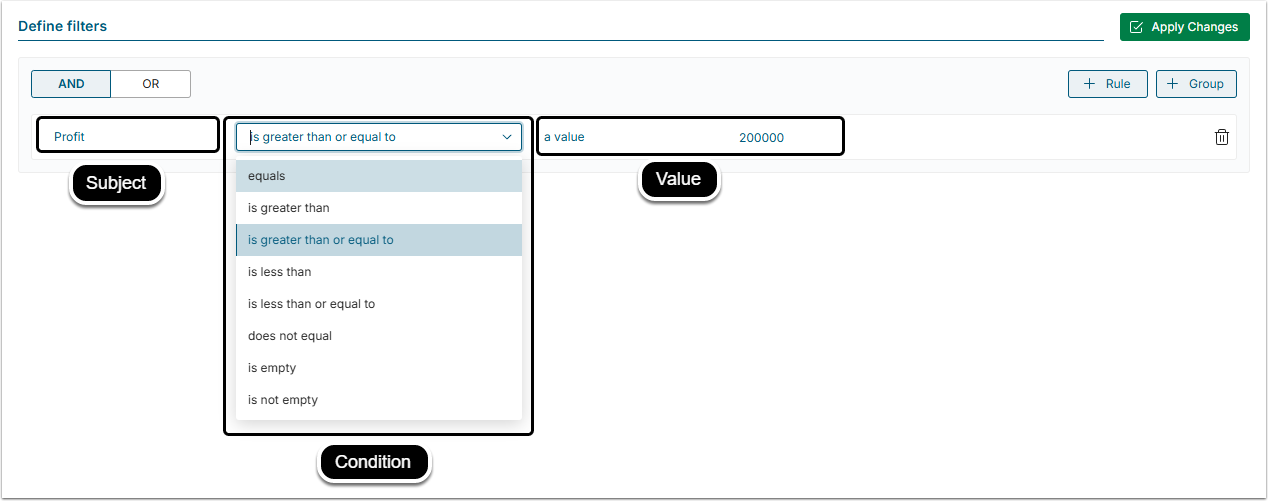
In addition to selecting specific fields, you can filter data using custom conditions. The process of creating a filter is similar to constructing a sentence: you choose a subject, comparison conditions and the values which are going to serve as a reference for filtering.
4. Types of Filters
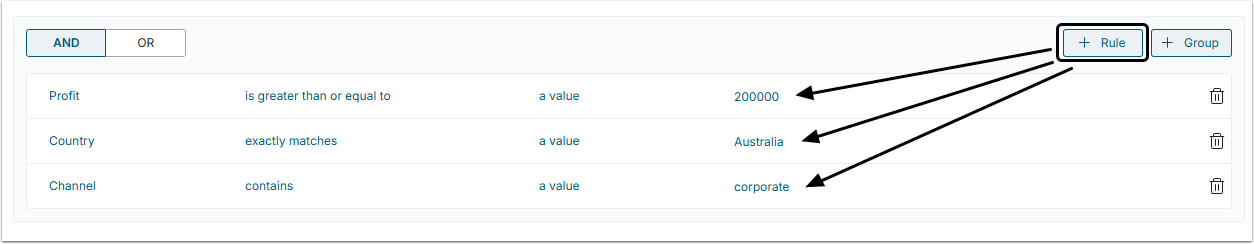
You can use filters to seed out the required information using conditional filtering. You may mix and match several simple Rules or compound filters (Groups) as defined in Create a Dataset View aggregated via [AND/OR] operators to focus on a highly specific data slice. The Results set will be displayed right on the same page.
5. AND/OR Operators
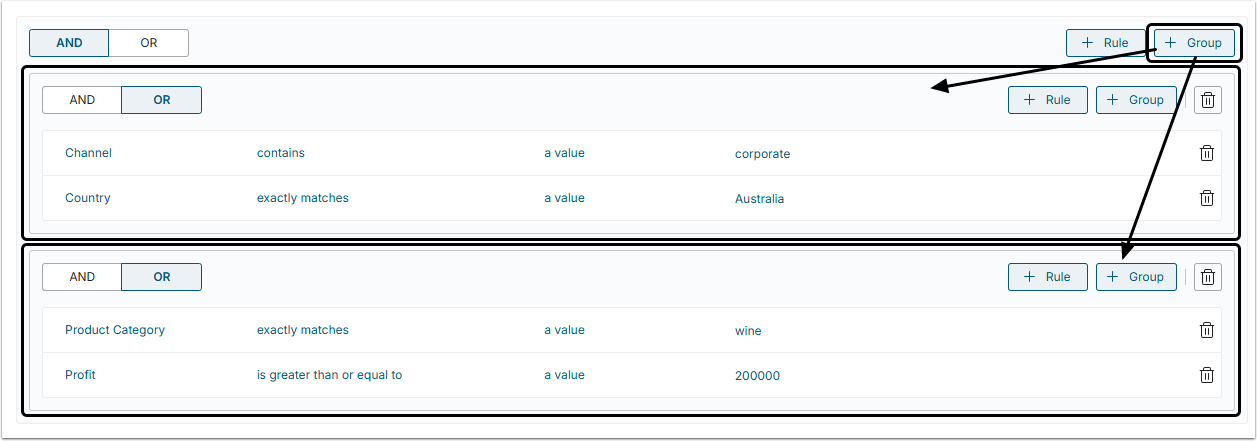
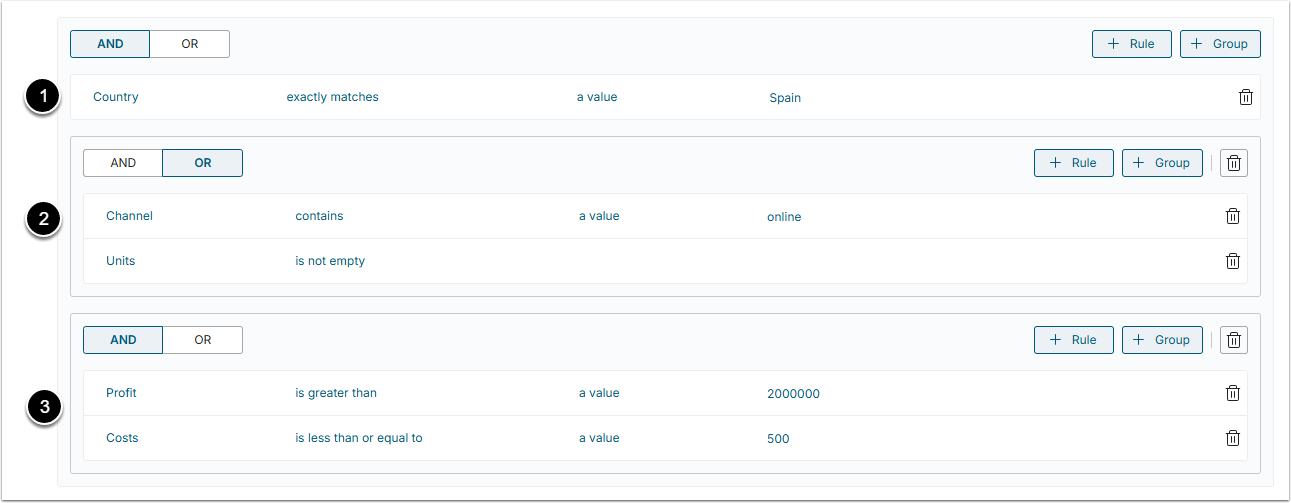
When you're using multiple Rules and Groups of conditions, you can use an AND/OR switches. You can not mix and match AND/OR for the set of applied filters but if you add a group of conditions, you may apply an alternative operator to it.
In the example below the following filters are applied to a Dataset. All of them are aggregated by the AND operator, meaning that all of 3 filters should be TRUE:
- Simple Rule;
- A Group of 2 conditions aggregated by the OR operator (ANY of 2 conditions should be TRUE);
- A Group of 2 conditions aggregated by the AND operator (ALL of conditions should be TRUE).
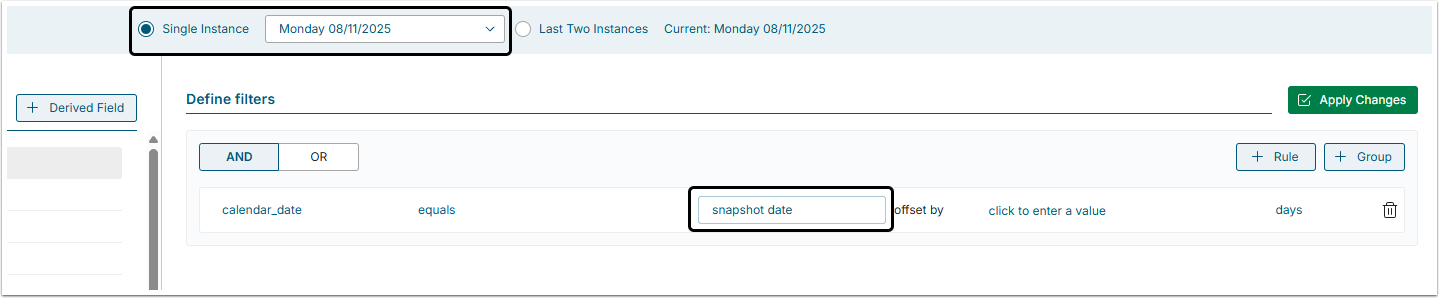
6. Comparing Dataset Date Fields to Snapshot Dates
Snapshot date is the date when the Dataset has been collected or updated.
Datasets may be:
- Single Instance: Shown only when the Dataset has been collected (as shown in the picture below).
- Multi-Instance (Snapshot dataset): Keeps history of Data updates.
User can filter on a date field by comparing the field to the Dataset effective date for a single instance or multi-instance Dataset.
7. Tracking Changes
You can compare the data from the current period to the prior period to highlight changes. For more details refer to the Snapshot Datasets Overview article.
8. Saving Field Selection and Applied Filters as a Separate View
There is no need to apply the same filters to review the same Results set later. After setting the Filters the User can save the Results set with selected fields and applied filters as a separate View by clicking [Save As View]. To learn more about Views, refer to the Create a Dataset View article.