Custom Scripts allow collecting specified data from Metric Insights and distributing it via bursts and alerts on various Notification Schedules.
- For details on writing Custom Scripts, see Basic Practices for Custom Scripts Developers and Slack Burst Example section of this article
Table of contents:
1. Create New Custom Script
Access Admin > System > Custom Scripts
The list page containing all Custom Scripts available in the system opens.
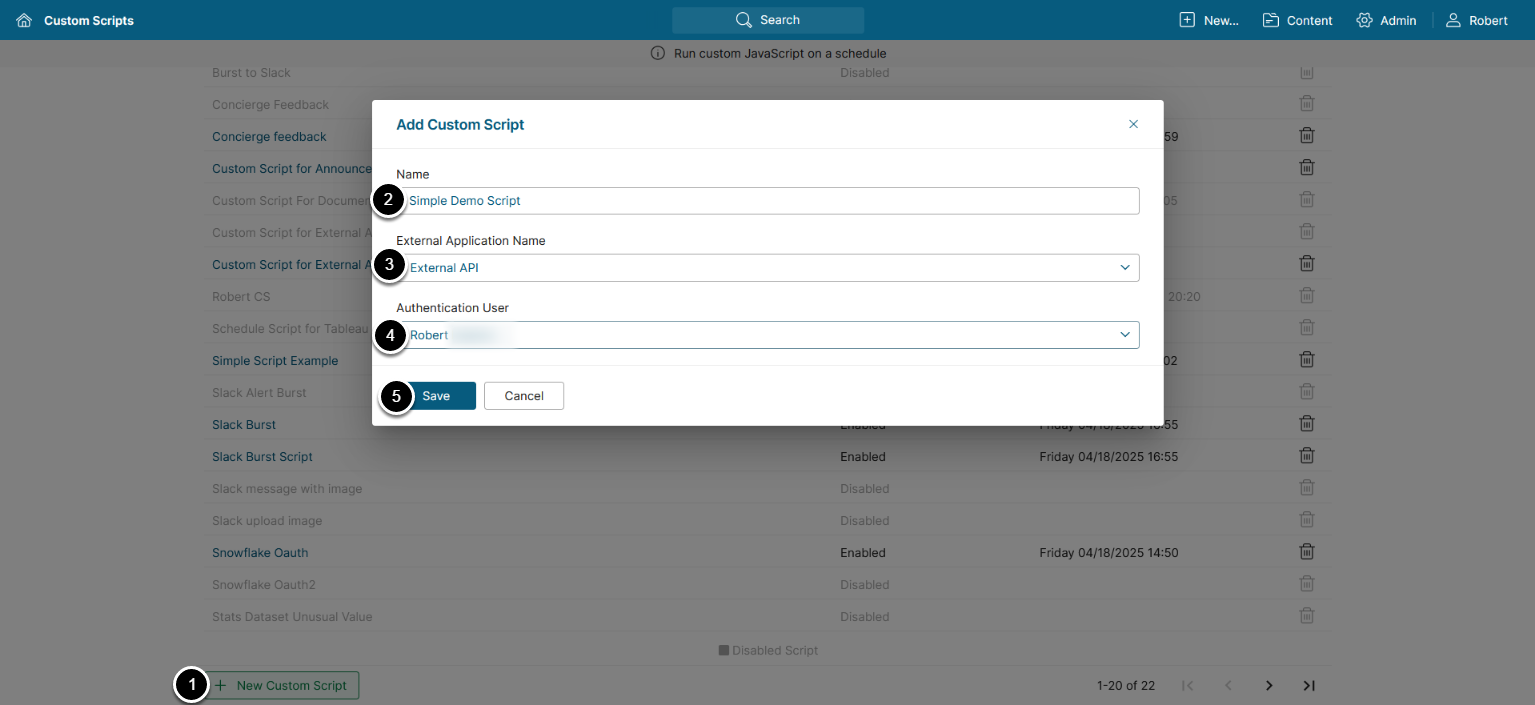
- Below the grid, click [+ New Custom Script]
- Name: Enter a name for the Custom Script
- External Application Name: Choose an External Application to automatically generate an API token for the Custom Script
- Authentication User: Choose a User on whose on behalf the Custom Script will act
- [Save]
NOTES:
- The API token is generated automatically on the background using the External Application's credentials and the Authentication User's username, and is required for the Custom Script to perform any actions in Metric Insights.
- The External Application settings control the Custom Script's access to the User API calls and to all API calls from external websites.
- The Custom Script will act on behalf of the Authentication User; e.g., if the Custom Script creates a new element, it will be displayed as created by the Authentication User.
2. Add Parameters
Access the Info tab
Parameters are Custom Scripts' variables that can be assigned different values. To add a Parameter:
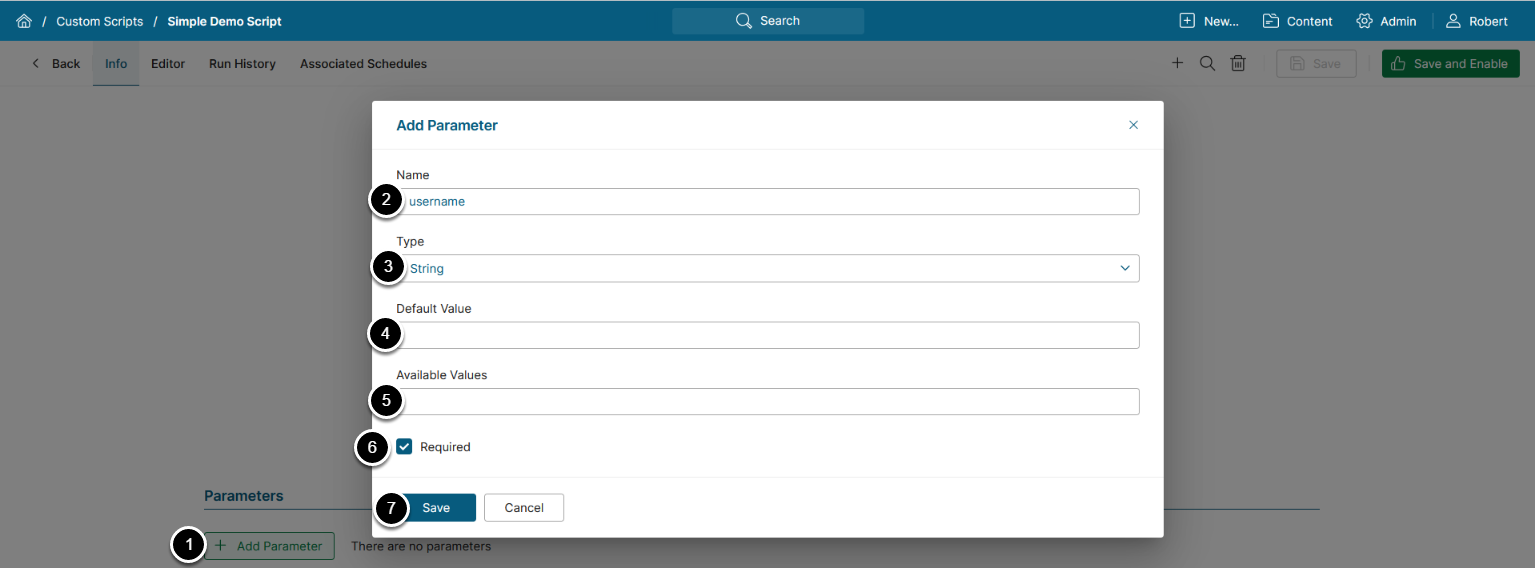
- [+ Add Parameter]
- Name: Enter a name for the Parameter
- Type: Choose a value type for the Parameter
- Default Value (optional): Enter a default value for the Parameter
- Available Values (optional): Enter a comma-separated list of available values
- Required: Activate the checkbox to make the Parameter required
- [Save]
3. Add a Parameter Set
Parameter Sets are especially useful when a Custom Script needs to be executed with different Parameter values. They represent sets of values assigned to Custom Script's parameters. To add a Parameter Set:
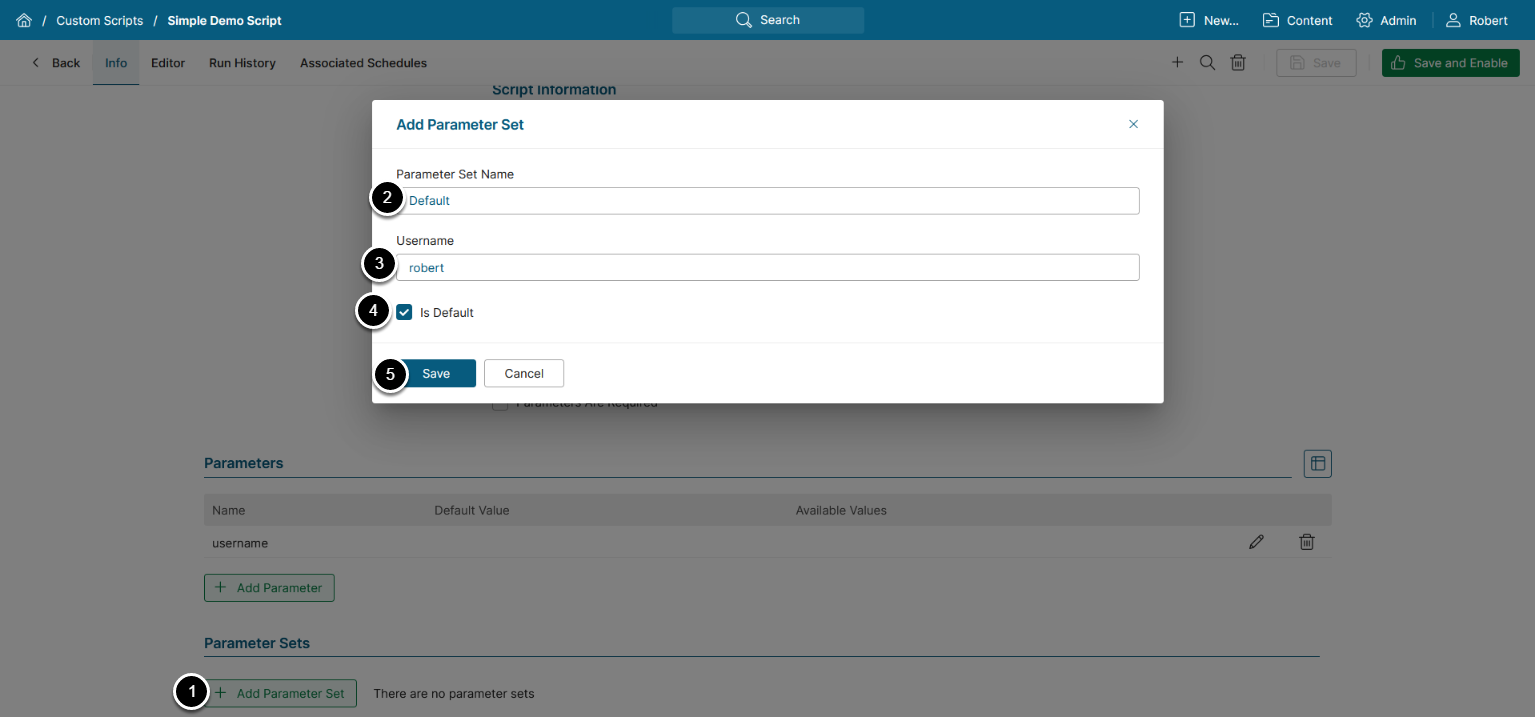
- [+ Add Parameter Set]
- Parameter Set Name: Enter a name for the Parameter Set
- Enter values for the Parameters
- Specify whether or not this Parameter Set is Default
- [Save]
4. Enter Custom Script Code
Access the Editor tab
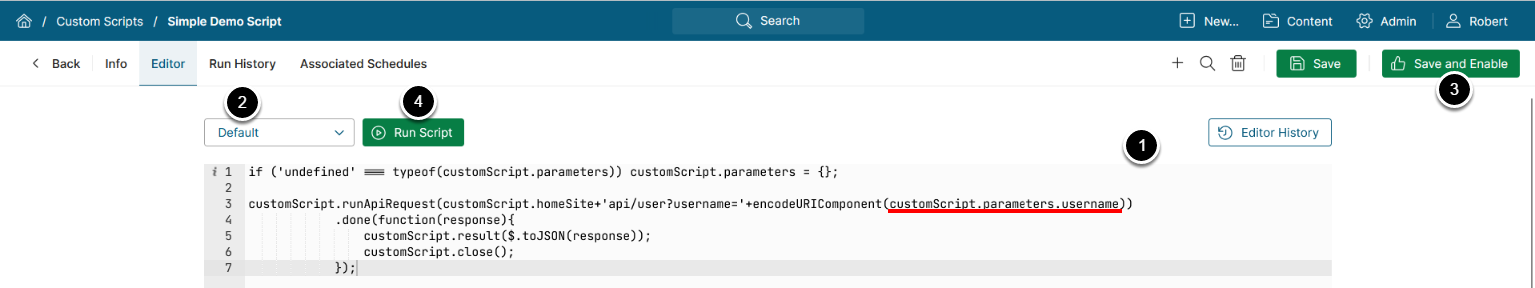
- Enter your script's code
- Access Script Parameters using dot notation:
customScript.parameters.<parameter_name>
- Access Script Parameters using dot notation:
- Choose a Parameter Set
- [Save and Enable]
- [Run Script]
For details on writing Custom Scripts, see Basic Practices for Custom Scripts Developers.
5. Set a Schedule
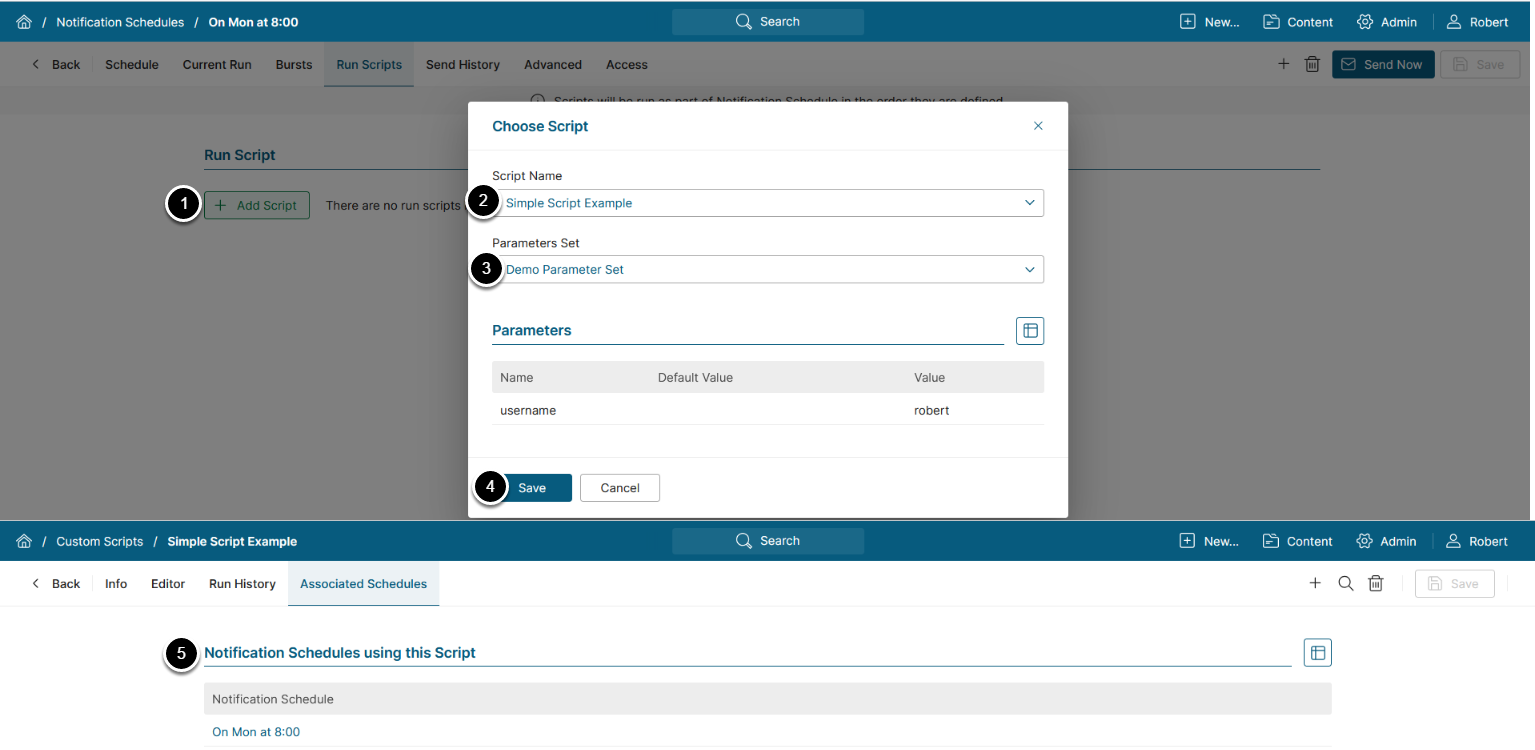
Access Admin > Distribution > Notification Schedules, select a Notification Schedule, access the Run Scripts tab
To run your Custom Script on a specified schedule:
- [+ Add Script]
- Script Name: Choose a Custom Script that will run on the Notification Schedule
- Parameter Set: Choose a Parameter Set with which the Custom Script will run
- [Save]
- The schedules on which the Custom Script will be executed are displayed on the Associated Schedules tab of the Custom Script
6. Slack Burst Example
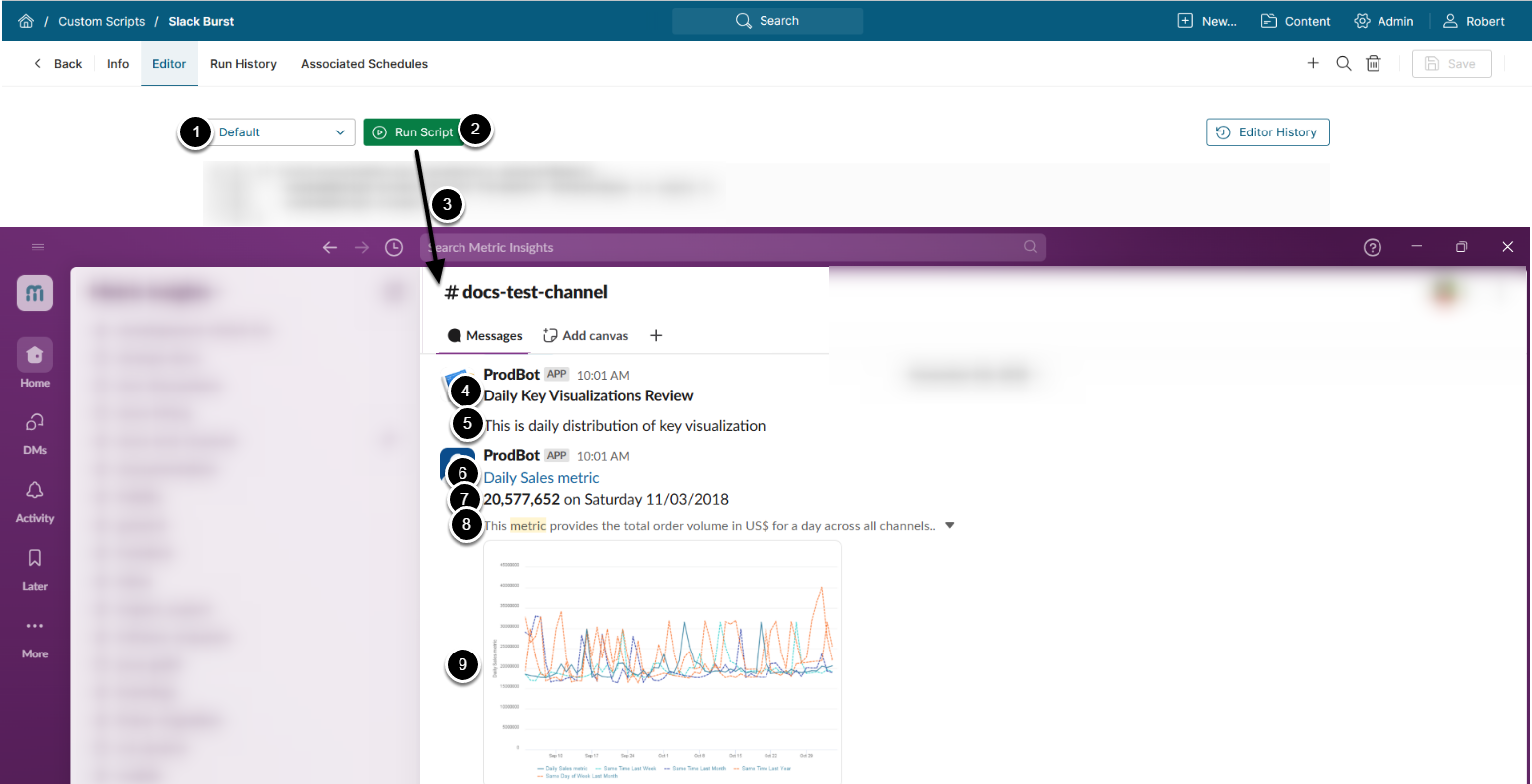
Let's consider a more complex use case on the built-in Slack Burst example, where the Dataset's data is sent to a Slack channel via the Custom Script.
Actions performed by the Custom Script to burst to a Slack channel:
- Send a request to the Dataset API to obtain a list of available Datasets
- Iterate over the Datasets list to find the needed Dataset by name
- Iterate over the Dataset's instances to find the instance, whose date is equal to yesterday
- Send the Dataset instance's data to a Slack channel
To be able to reproduce this use case, connect your Slack account to MI:
This example demonstrates the usage of Custom Scripts; however, if you want to create a Burst to a Slack channel, a simple approach exists:
- See Bursting to a Slack Channel for details
6.1. Open Slack Burst Custom Script
Access Admin > System > Custom Scripts
Find the Slack Burst Custom Script and open it.
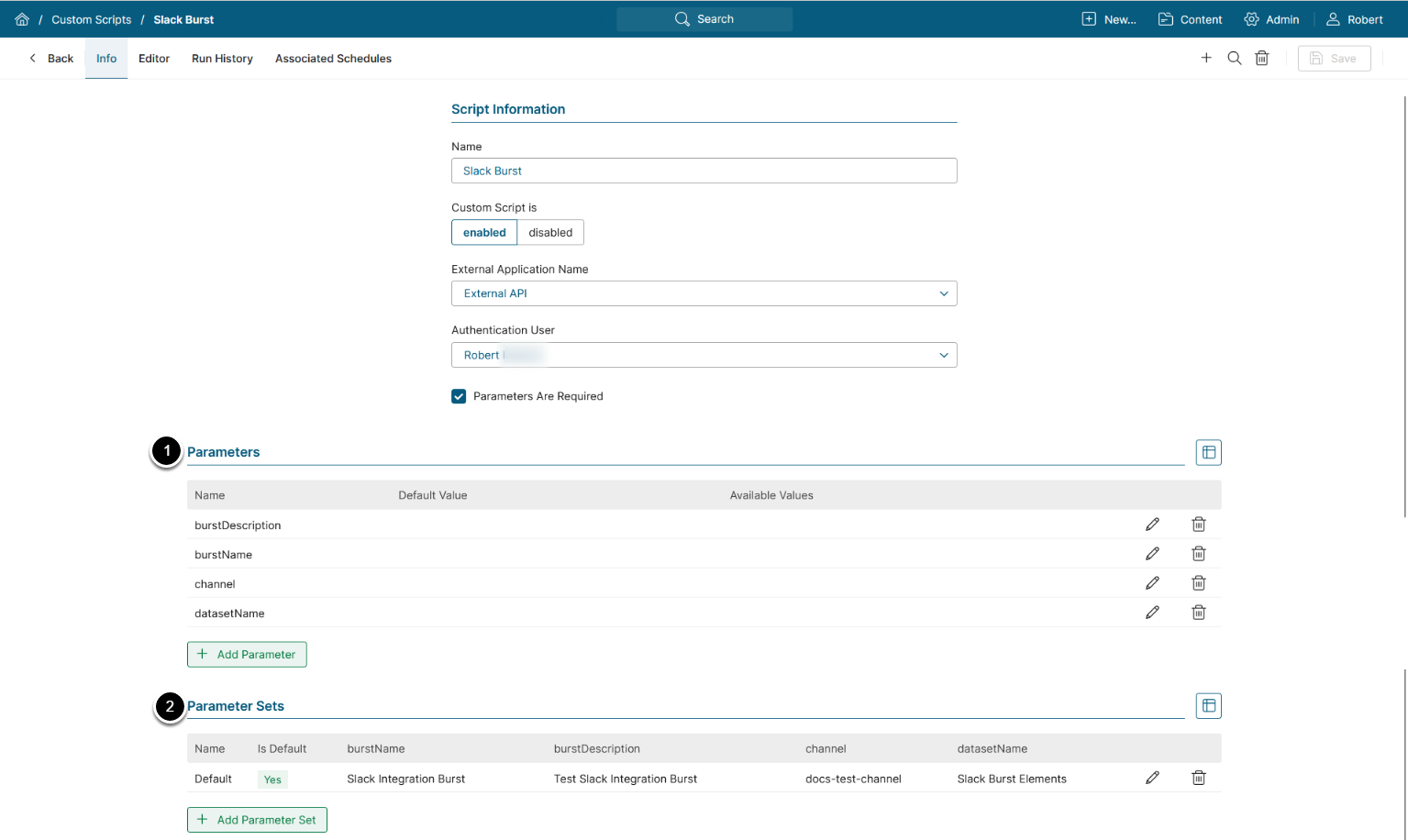
6.2. View Parameters and Parameter Sets
- The Parameters that are used in the Slack Burst Custom Script:
- burstDescription: A text message that is sent to the specified Slack channel
- burstName: A "header" of the message that is sent to a Slack channel
- channel: The Slack channel where the message is sent to (to see the list of available channels, access Admin > Distribution > Slack Integration > Channel tab)
- datasetName: The Dataset that contains information about the Elements, whose info is sent to a Slack channel
- The provided values for Parameters are displayed upon Parameter Sets
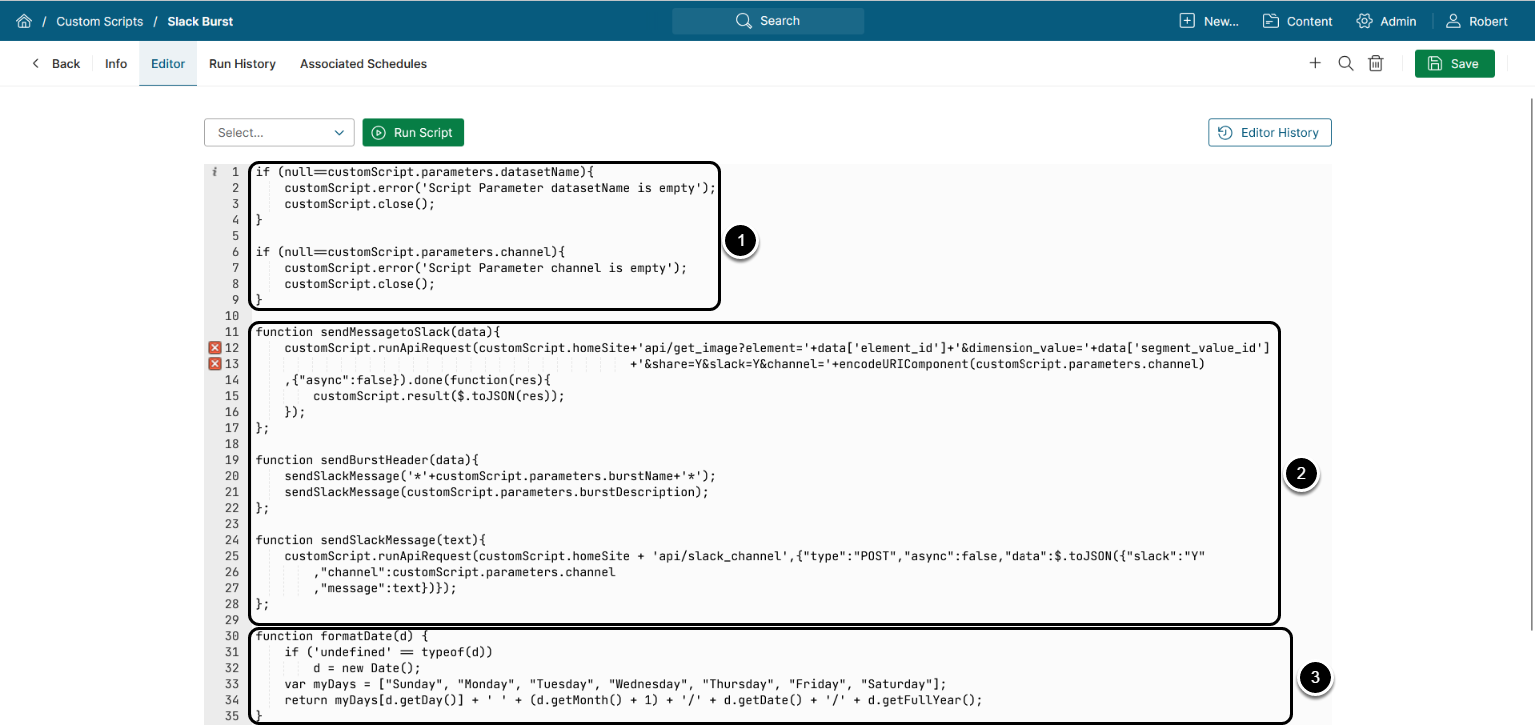
6.3. View Custom Script Code
For more details on MI Dataset API, see Dataset API.
- Validation of the datasetName and channel parameters
- Functions that send information to the Slack channel:
-
sendMessagetoSlack(): Sends a request to<hostname>/api/get_image?element=<element ID>&dimension_value=<dimension ID>&share=Y&slack=Y&channel=<slack_channel_name>, which triggers a message to the Slack channel with the element's information -
sendBurstHeader(): UsessendSlackMessage()function to send the burst name and description in a text format (the values of burstName and burstDescription) to a Slack channel -
sendSlackMessage(): Sends a text message to a Slack channel (a POST request to the MI API)
-
-
formatDate(): Returns Dataset's date in a human-readable format and is used to display an error message if no data is found for a Dataset
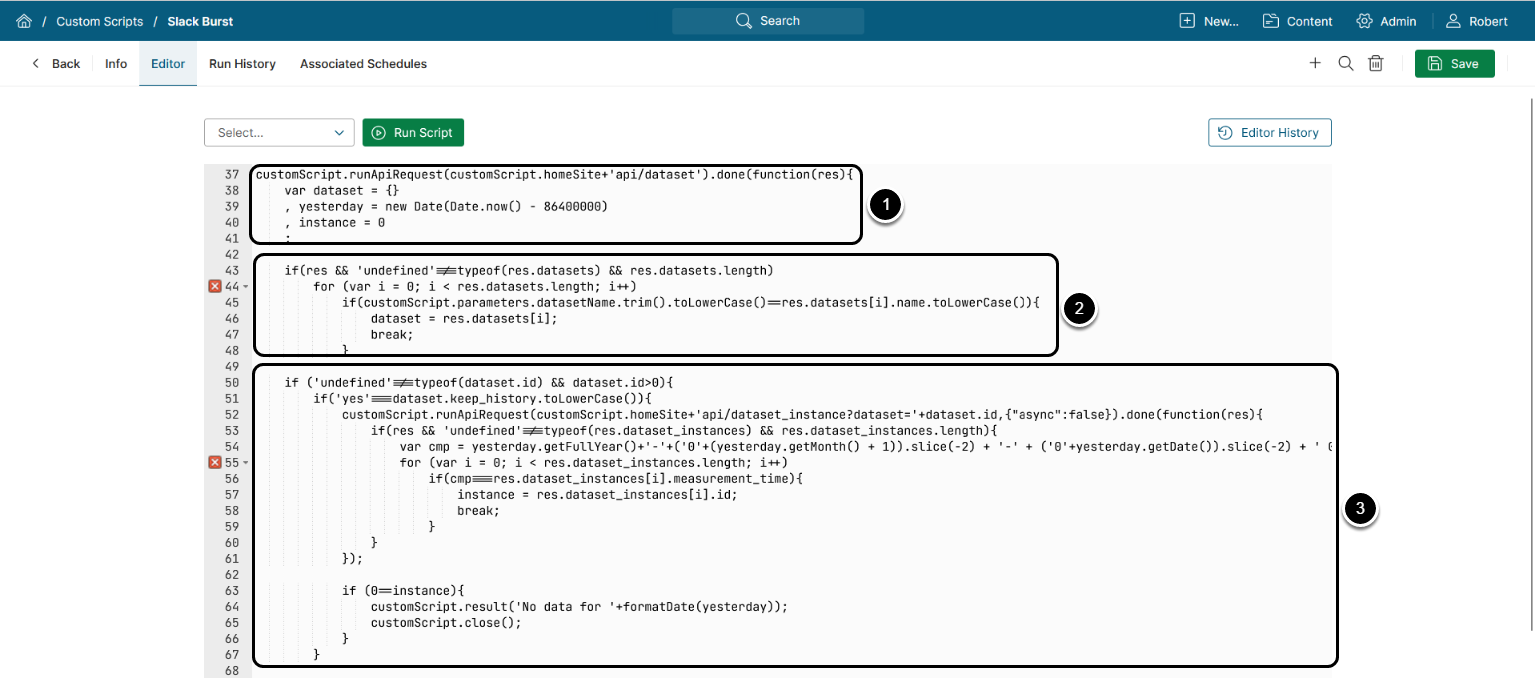
6.3.2. Finding the Dataset and Instance by Name and Date
- Sending a GET request to
/api/datasetand performing actions on the received response data. All the next commands are executed within this function's body- The
datasetobject encapsulates all the obtained Datasets - The
instancevariable represents a single Dataset
- The
- Iterating through the obtained Datasets until a Dataset whose name corresponds to a name from the datasetName parameter is found. Its value is assigned to the
datasetobject - Sending a GET request to
/api/dataset_data?dataset=<Dataset ID>to obtain an object encapsulating the Dataset's instances
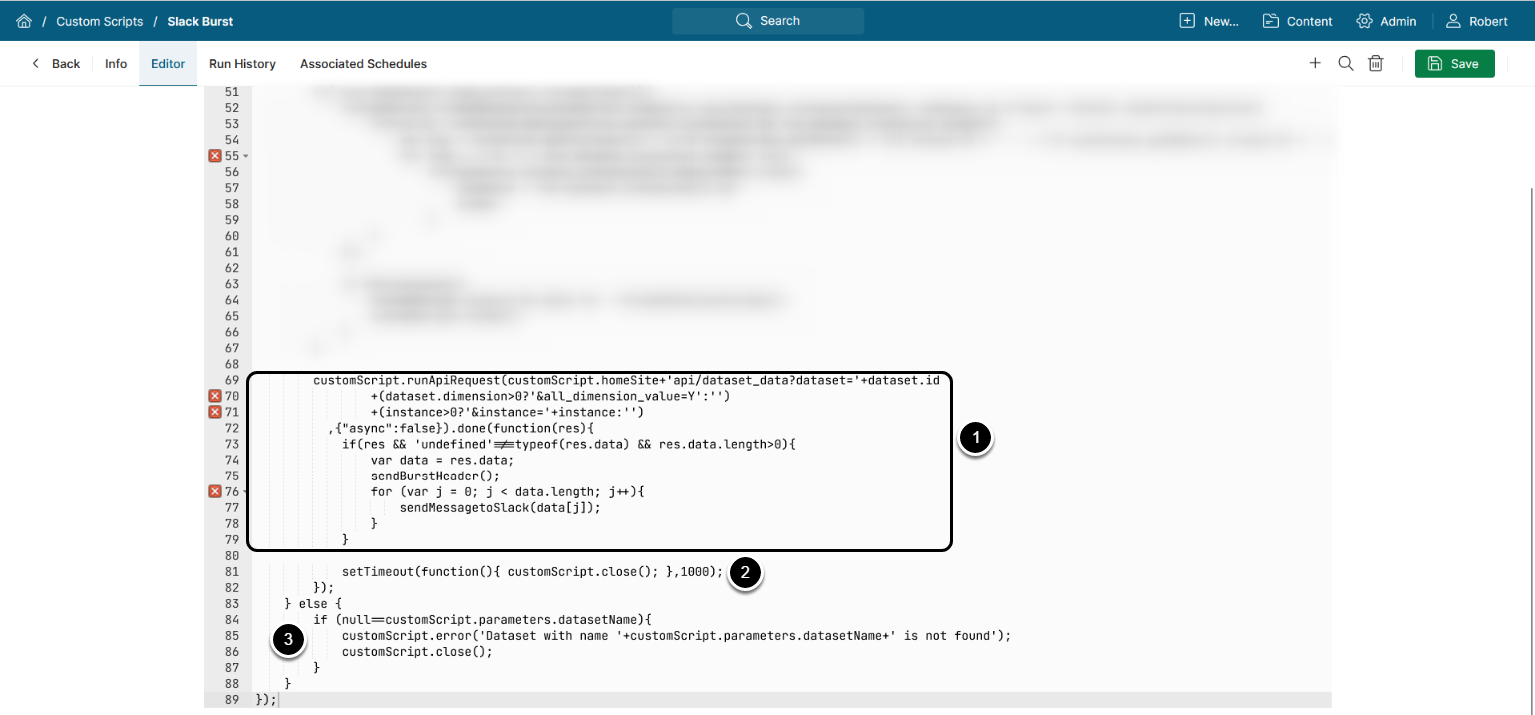
6.3.3. Sending Dataset Data to Slack
- Sending GET request to
/api/dataset_data?dataset=<Dataset ID>to obtain Dataset instance data, then:- Assigning instance data to the
dataobject - Sending burst text to a Slack channel by calling
sendBurstHeader() - Iterating over collected instance data and sending it to a Slack channel
- Assigning instance data to the
- End Script execution
- Log error message if no Dataset was found